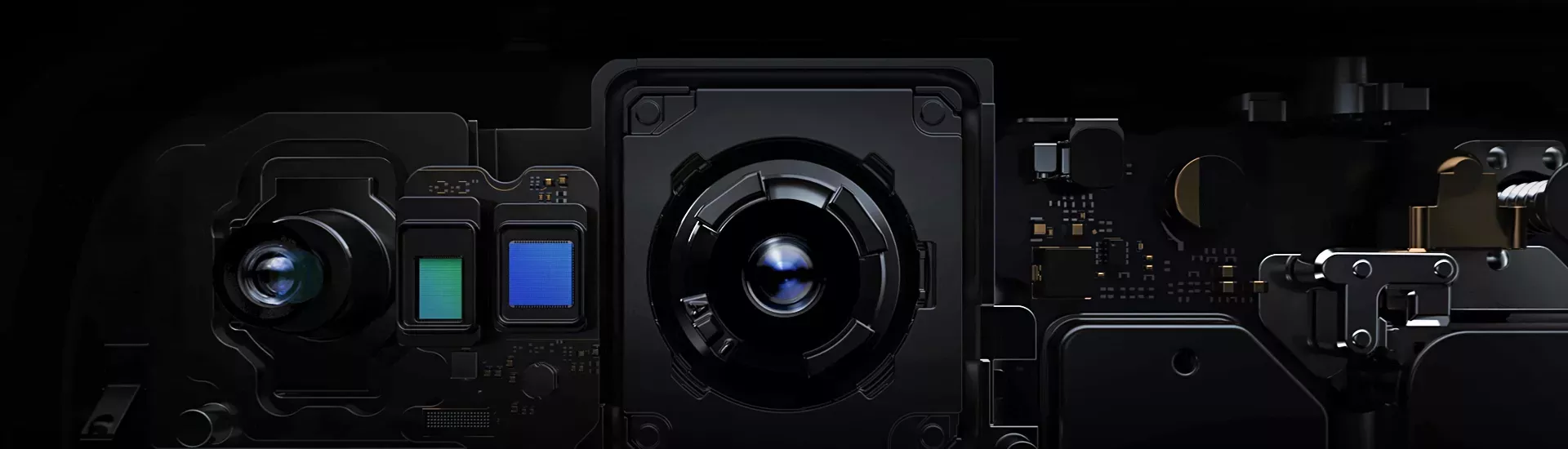
The core chip of the camera – CMOS image sensor
2023-09-23 1279 YXF
A CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) image sensor’s operating concept was envisioned in the second half of the 1960s, but the device was not commercialized until microfabrication technology evolved sufficiently in the 1990s. CCD (charge coupled device) or CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) image sensors are often used in today’s digital cameras and mobile phones.

CCD and CMOS are both semiconductor devices that function as “electronic eyes.”
They both employ photodiodes, but their production processes and signal reading methods differ. Although CCD technology was popular at initially owing to higher sensitivity and picture quality, CMOS sensors began to outnumber CCD sensors in shipping volume beginning in 2004.
Data rate is faster than CCD.
An array of capacitors in a charge-coupled device (CCD) image sensor carries an electric charge according to the light intensity of a pixel. Each capacitor’s contents are transferred to its neighbor via a control circuit, and the last capacitor in the array empties its charge into a charge amplifier. CCD sensors are known for their bucket-brigade data transmission method.
A complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) image sensor
on the other hand, contains a photodiode and a CMOS transistor switch for each pixel, which allows the pixel signals to be amplified separately. The pixel signals may be accessed directly and sequentially, considerably faster than a CCD sensor, by manipulating the matrix of switches. Another advantage of having an amplifier for each pixel is that it decreases the noise that arises while reading the electrical signals converted from collected light.
CMOS image sensors are less expensive to manufacture than CCD image sensors because existing semiconductor manufacturing equipment may be reused for their production.Unlike CCD sensors, which utilize high-voltage analog circuits, CMOS sensors use a smaller digital circuitry that consumes less power and is, in theory, devoid of smear (vertical white streak in a bright-light image) and blooming (corruption of images such as white spots). Because logic circuitry can be incorporated onto the chip during the manufacturing process, CMOS sensors with an on-chip image processing circuit are being developed for applications such as image recognition and artificial vision, with some devices currently in use.